Master Essential QA Tools and Skills
From how to write test cases to how to automate them.
Master Leading Tools in the Industry.

One of a Kind Program
Designed by Software QAs for future Software QAs.
Interview Focused from day 1.
Real Projects for real valuable learning and Practice.
1 on 1 Mentorship
Private 1 on 1 Mentorship sessions.
Job Readiness, Mock Interviews and preparations for real interviews.

Internship
Working with QA engineers in Real life environment.
Working on real projects.
Solving Real Problems.

62+hours of live learning

97%
Graduation Rate/batch

75%Got hired within 3 months
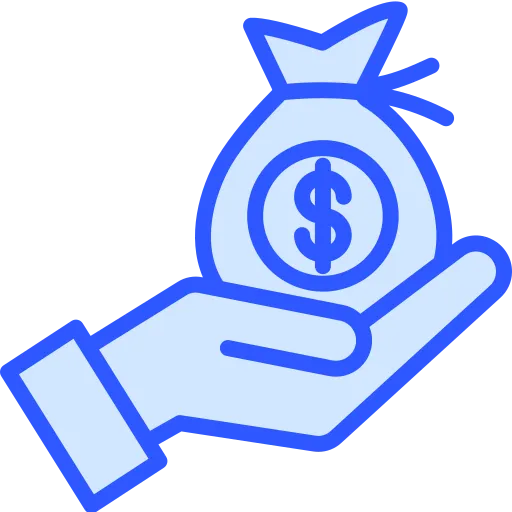

$121,000Average Salary.
For Beginners
Quality Assurance Analyst
Start a career in Software Testing with no prior coding experience in just 2 months.
4 Weeks | 18 Hours of Live Classes | Internship | Mentorship
For Advanced
Software Development Engineer in Test
Launch your career in IT right to six figures with SDET program
14 Weeks | 60 Hours of Live Classes| Internship | Mentorship
Not sure where to Begin?
Our Program Advisor will be more than happy to call you and answer your Questions.

From Uber driver to Software Automation Test Engineer.
Jared Reed used to drive Uber in Toronto, he always felt there was something more he could do.
Despite having no tech background, Jared enrolled in the Software Development Engineer in Test program. Through determination and hands-on learning, he transitioned from the driver's seat to a thriving career in tech. Today, Jared works as an Automation Test Engineer, fully remote, enjoying a fulfilling job with the flexibility and stability he always wanted.
Who hires our students?




And Many more...
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Formal Education Like a Degree and Experience Required to Become a Software Tester?
Formal Education: A degree in computer science, engineering, or a related field can be beneficial but is not always required. Many successful testers come from diverse educational backgrounds.
What’s more important is understanding software testing principles and acquiring relevant skills.
Experience: While prior experience can be advantageous, it is not mandatory to start a career in software testing. Many entry-level positions and SkillUp programs provide the necessary training and practical experience to get started.
What skills do I need to succeed in software testing?
To succeed in software testing, you need a combination of technical, analytical, and soft skills:
Technical Skills:
Understand SDLC/STLC and testing methodologies.
Proficiency in test automation tools (e.g., Selenium, JUnit).
Basic programming skills in languages like Java or Python.
Familiarity with version control (e.g., Git) and CI/CD pipelines.
Knowledge of SQL for database testing and experience with API testing tools (e.g., Postman).
Analytical Skills:
Attention to detail and critical thinking.
Strong problem-solving abilities.
Soft Skills:
Effective communication and documentation.
Collaboration and teamwork.
Time management and adaptability.
We offer a proven program that teaches all of these essential skills, ensuring you're well-equipped to excel in software testing.
What is the difference between manual testing and automation testing?
Manual Tester:
A manual tester performs tests on software applications without the use of automation tools. They manually execute test cases, explore the application, and identify bugs. This type of testing is often used for exploratory, usability, and ad-hoc testing where human judgment is crucial.
Automation Tester:
An automation tester uses specialized tools and scripts to automate repetitive testing tasks. Automation testing is ideal for regression testing, performance testing, and scenarios that require executing the same set of test cases repeatedly. Automation testers typically have programming skills and work to increase testing efficiency by reducing manual efforts.
In summary:
Manual testing is hands-on and requires human insight, while automation testing uses tools to perform tests more quickly and consistently. Both approaches are essential in ensuring software quality.
How much money Software Testers earn?
Manual Testers:
United States:
On average, manual testers earn between $70,000 to $80,000 per year.
Independent contractors - Manual Testers typically charge $40 to $50 per hour, which can translate to $80,000 to $100,000 per year depending on hours worked and project availability.
Canada: Manual Testers typically earn between CAD $60,000 to $75,000 per year.
Independent contractors - Manual Testers usually charge CAD $30 to $50 per hour, leading to earnings of CAD $60,000 to $100,000 per year.
Automation Testers:
United States: Automation Testers generally earn between $80,000 to $120,000 per year.
Independent contractors - Automation Testers generally charge $50 to $100 per hour, potentially earning $100,000 to $200,000 per year.
Canada: Automation testers typically earn between CAD $75,000 to $105,000 per year.
Independent contractors - Automation Testers typically charge CAD $50 to $90 per hour, resulting in annual earnings of CAD $100,000 to $180,000.
Note:
Salaries can vary widely based on factors like experience, location, and industry. Automation testers often command higher salaries due to their specialized skills.
Independent contractors often have the potential to earn more than salaried employees due to the flexibility in setting their rates and taking on multiple projects.
What career opportunities are available in software testing?
Manual Tester: Start as a Junior or Entry-Level Tester and advance to Senior Manual Tester roles. Specialize in areas like usability testing, exploratory testing, or becoming a Test Lead/Manager.
Automation Tester: Begin as an Automation Tester and grow into Senior Automation Engineer roles. Opportunities to specialize in specific tools or frameworks and lead automation projects.
Quality Assurance (QA) Analyst/Engineer: Focus on improving overall software quality by integrating testing processes throughout the development cycle.
Test Lead/Manager: Oversee testing teams and ensure project quality standards. Responsible for planning, coordinating, and executing testing strategies.
Test Architect: Design and implement testing frameworks and strategies at an organizational level. Mentor and guide testing teams and help integrate testing best practices across the company.
DevOps Engineer: Leverage automation and continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) practices to enhance the software delivery pipeline. Evolve into roles that blend testing with development and operations.
Consultant/Trainer: Offer expertise as a testing consultant or trainer, helping organizations improve their testing practices. Opportunities to teach or mentor new testers, or develop training programs.
Independent Contractor/Freelancer: Work independently, offering specialized testing services to various clients. Freedom to choose projects and set your rates, with potential for high earnings.
In summary: A career in software testing offers a wide range of opportunities, from specialized testing roles to leadership positions, and even independent consulting or freelancing.4
Upcoming Webinar
Join our webinar to explore the world of Software Testing, discover the industry, learn about the role, and find out if it's the right career path for you.

Our Students Recommend Us!

SkillUp gave me the confidence to apply for jobs, appear in interviews and then perform at the job. The tools and Framework used was extremely practical.

Waleed Khan

Mentorship sessions really helped me gain confidence for interviews. At the start of the Interview, I was actually waiting for them to ask me "Tell us about yourself?" LOL

Kristin Watson

My Transition from Manual QA to Automation QA was made simple.





